Disclaimer: I'm not an electrical engineer by training so don't blame me if I get any inference wrongly in my post. 😄
Introduction
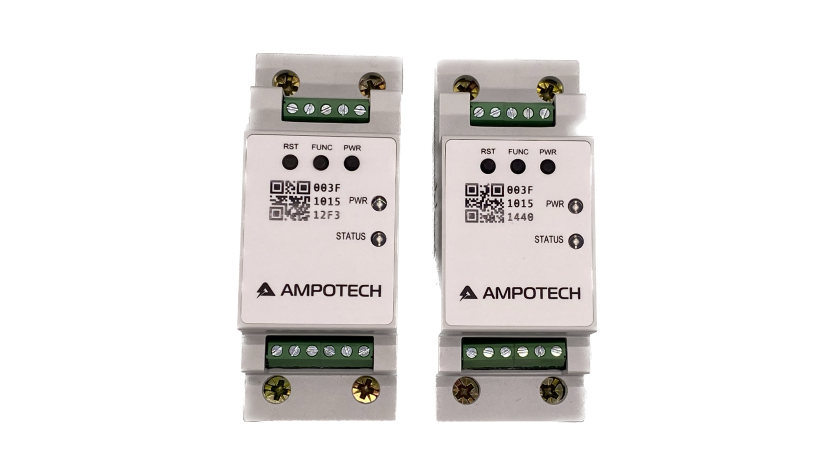

My new house came with this wireless IoT power meter installed in my DB box. I did some research and found several articles talking about this device:
- https://www.straitstimes.com/tech/ampotechs-smart-device-to-track-your-energy-usage

What is AmpoHub
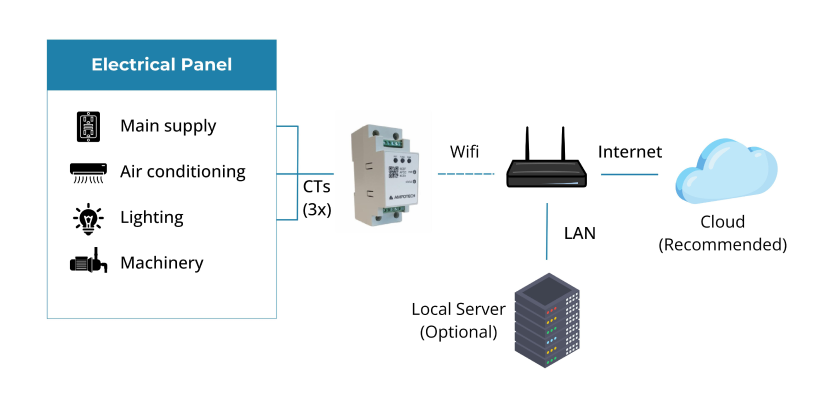
The AmpoHub is a compact, wireless-enabled power meter and IoT gateway. The device is installed in low-voltage electrical distribution panels and has three input channels for current transformer (CT) sensors and three inputs, allowing it to measure single-phrase or three-phrase power. The AmpoHub also has a built-in WiFi module and data logging capability and supports remote device management and troubleshooting through the AmpoCloud platform. With its small size, second-level data rate, and IEC 62053-21 Class 1 accuracy, AmpoHub is suitable for monitoring individual machines, or for metering use cases in residential, commercial, and industrial sites.
What can the AmpoHub monitor?
- Air conditioner
- Freezer
- Cold room
- Pump
- Fan
- Oven
- Air compressor
- Solar inverter
- F&B cooler/heater
- Wall outlet circuit (IT equipment)
- Lighting circuit (Indoor, outdoor)
Use Case
- Application-based uses in solar power monitoring and trip-detection.
- Equipment-specific power monitoring for motors, lighting and airconditioning.
- IoT-enable power monitoring in smart homes and industry 4.0 settings.
Specifications - Measurements
| Number of Channels | 3 Current, 3 Voltage | |
|---|---|---|
| Parameters Measured (Each Channel) | Current (A), Voltage (V) Power (kW), Energy (kWh), Power Factor (dimensionless), Frequency (Hz) | Support Bi-directional energy reading |
| Reporting Rate | Adjustable | |
| Default Reporting Rate | 0.2Hz (report every 5 sec) | |
| Measurement Type | True RMS (8kHz sampling) | |
| Measurement accuracy | Active Power: Class 1 Reactive Power: Class 2 |
Connecting to AmpoHub
I then did some further research and found this http://amposense.com detailing the instructions to connect to the AmpoHub.
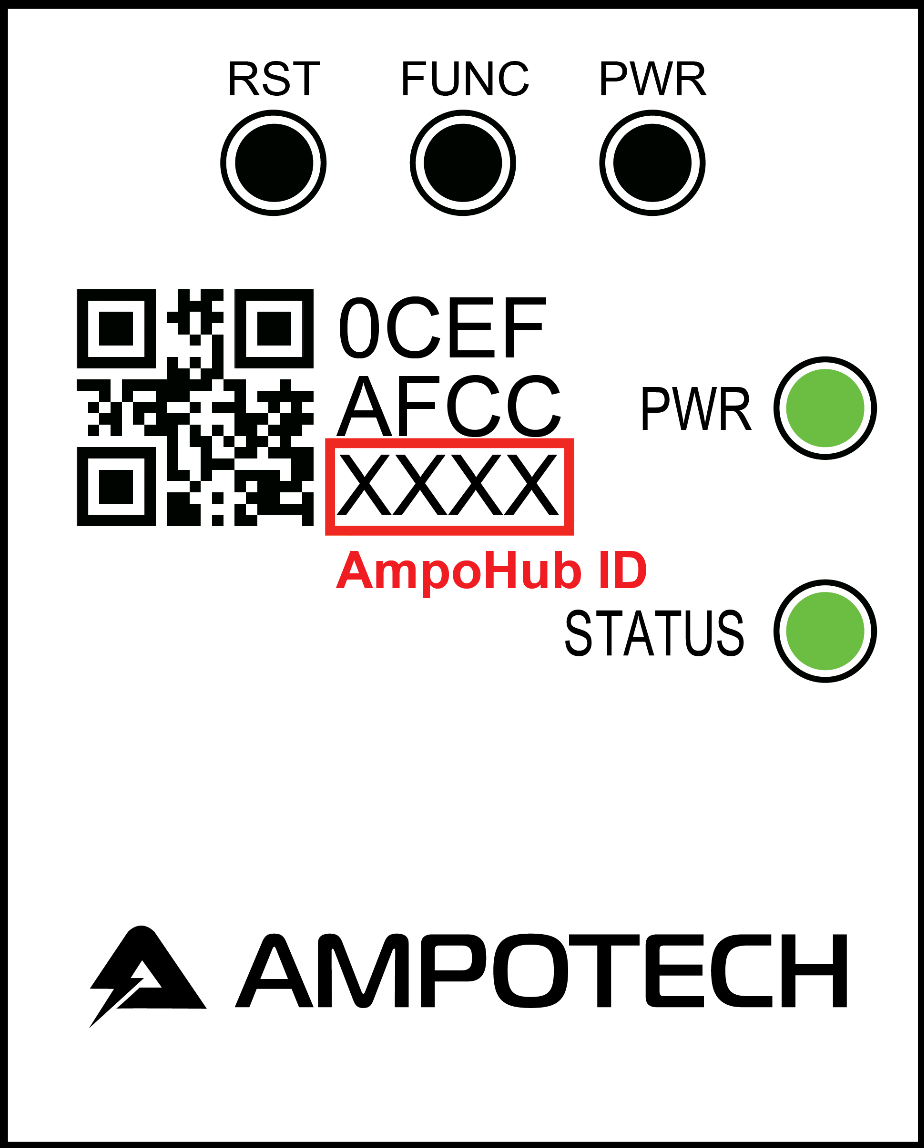
I searched my Wifi networks and found a SSID with AmpoHub-XXXX that correspond to my AmpoHub ID. I then tried to connect to it.
However, no password was given to me during the keys collection. I tried different combination of "password", "admin", etc, until I got the default password of "ampotech". 😄
After getting connected, I then visited http://192.168.8.1/ on my browser and successfully see the webui.
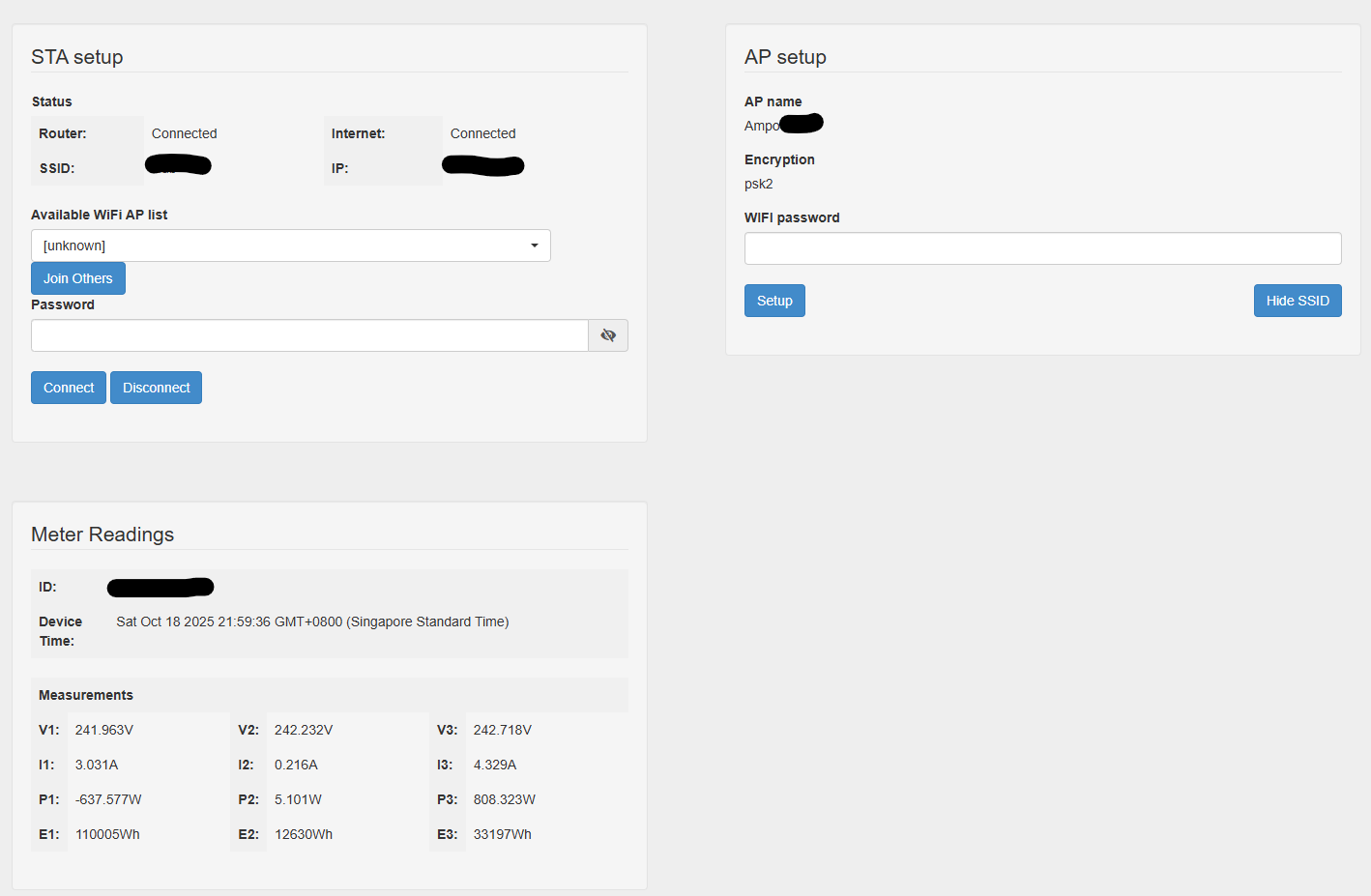
Trying to connect to my IoT Wifi network was a nightmare because the webui is designed to loop the get_measurement API call every 2s, resulting in the webpage being very unresponsive.
For the benefit of others, you can set your wifi using curl by executing the following command:
curl http://192.168.8.1/cgi-bin/setwifi?ssid=<your wifi ssid>&password=<your wifi password>Please remember to URL-encode the spaces if any in your SSID name.
Once it's done, you should be able to see your AmpoHub connected to your network and obtained an IP address.
You can now access AmpoHub without connecting to it's own Wifi SSID.
Getting Measurements
I opened up my Chrome Developer Tools and found that the WebUI is calling the following URL (http://<ampohub ip>/cgi-bin/get_measurement) every 2s to obtain the measurements.
To test it out, I tried using curl to obtain the JSON response:
curl -s http://<ampohub ip>/cgi-bin/get_measurementPoint to note: There's a non-standard header being returned in the response by the embedded web server that is causing programatic HTTP requests or Postman to fail. You have to sanitize or ignore the headers in your requests.
To illustrate, we execute the curl with verbose output:
alex@Alex-PC:~$ curl http://<ampohub ip>/cgi-bin/get_measurement -vvvv
* Trying <ampohub ip>...
* Connected to <ampohub ip> (<ampohub ip>) port 80 (#0)
> GET /cgi-bin/get_measurement HTTP/1.1
> Host: <ampohub ip>
> User-Agent: curl/7.81.0
> Accept: */*
>
* Mark bundle as not supporting multiuse
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Connection: Keep-Alive
< Transfer-Encoding: chunked
< Keep-Alive: timeout=20
< <M2.6&0832&4&480000: 777777:8b7:8b7:00/02/19&23:03:36@242432,242710,243190,2822,216,4298,16,-530624,5170,803963,278510,-775,97,769,156,-3764,4375,2599,2929,110136,12631,33368,110126,4996,0,12552,33283,22907,110136,79,85,87219,302567,-49464,444460,697563,684372,52665,1045330,1782368,1293,81,2019,13236,13251,13282,0,0,0,151,276,30,0,34458,24443,28444,54731,31065,2858,13606,31324,3393,21585,14838,23407,136107,36512,57283,229902>
< Content-Type: application/json
<
{"result":"success", "v1":"242432", "v2":"242710", "v3":"243190", "i1":"2822", "i2":"216", "i3":"4298", "in":"16",
"p1":"-530624", "p2":"5170", "p3":"803963", "pt":"278510", "e1":"110136", "e2":"12631", "e3":"33368", "et":"110126", "freq":"4996", "mcu_time":"xxxx00/02/19&23:03:36"}
* Connection #0 to host <ampohub ip> left intact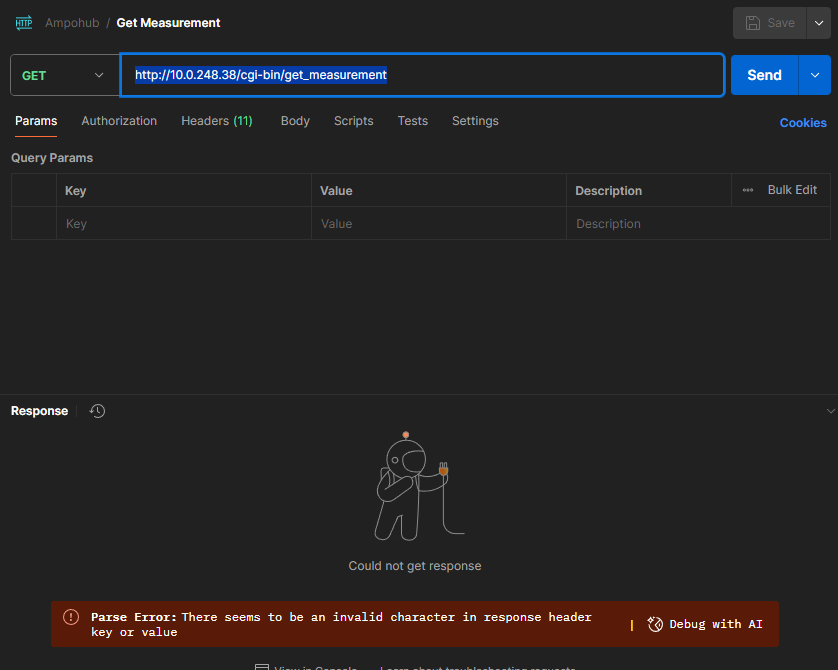
The JSON response will look like this:
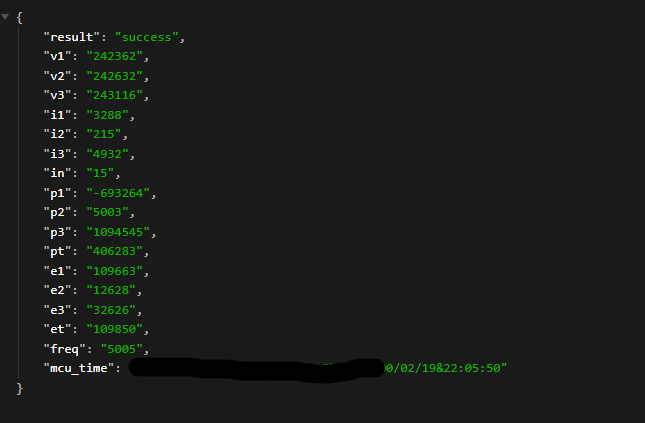
With the response above, I inferred that the field mapping will be as follows:
| Field | Mapping |
|---|---|
| v1 | Voltage Channel 1 (V) |
| v2 | Voltage Channel 2 (V) |
| v3 | Voltage Channel 3 (V) |
| i1 | Current Channel 1 (A) |
| i2 | Current Channel 2 (A) |
| i3 | Current Channel 3 (A) |
| in | Neutral Current (A) |
| p1 | Power Channel 1 (W) |
| p2 | Power Channel 2 (W) |
| p3 | Power Channel 3 (W) |
| pt | Total Active Power (W) |
| e1 | Energy Channel 1 (Wh) |
| e2 | Energy Channel 2 (Wh) |
| e3 | Energy Channel 3 (Wh) |
| et | Total Energy (Wh) |
| freq | Line Frequency (Hz) |
| mcu_time | Firmware/Version & Timestamp |
Creating Sensors in Home Assistant
With the above information, I proceed to create the sensors in Home Assistant. I chose command_line sensor instead of RESTful sensor because of the header issue I mentioned above. Maybe I will fix the header in future, but for now, I prefer to have a working monitoring in place first.
Add the following lines in your configuration.yaml:
command_line:
- sensor:
name: AmpoHub IoT Gateway
command: 'curl -s http://10.0.248.38/cgi-bin/get_measurement' # AmpoHub API URL
scan_interval: 5 # seconds
command_timeout: 5 # seconds
value_template: "{{ value_json.result }}"
json_attributes:
- v1
- v2
- v3
- i1
- i2
- i3
- in
- p1
- p2
- p3
- pt
- e1
- e2
- e3
- et
- freq
- mcu_timeAfter which, we have to expose the sensors in the Templates. Add the following lines in your configuration.yaml again.
template:
- sensor:
# ---------- Voltages ----------
- name: "Phase L1 Voltage"
device_class: voltage
state_class: measurement
unit_of_measurement: "V"
state: "{{ (state_attr('sensor.ampohub_iot_gateway','v1')|float(0) / 1000) | round(1) }}"
- name: "Phase L2 Voltage"
device_class: voltage
state_class: measurement
unit_of_measurement: "V"
state: "{{ (state_attr('sensor.ampohub_iot_gateway','v2')|float(0) / 1000) | round(1) }}"
- name: "Phase L3 Voltage"
device_class: voltage
state_class: measurement
unit_of_measurement: "V"
state: "{{ (state_attr('sensor.ampohub_iot_gateway','v3')|float(0) / 1000) | round(1) }}"
# ---------- Currents ----------
- name: "Phase L1 Current"
device_class: current
state_class: measurement
unit_of_measurement: "A"
state: "{{ (state_attr('sensor.ampohub_iot_gateway','i1')|float(0) / 1000) | round(3) }}"
- name: "Phase L2 Current"
device_class: current
state_class: measurement
unit_of_measurement: "A"
state: "{{ (state_attr('sensor.ampohub_iot_gateway','i2')|float(0) / 1000) | round(3) }}"
- name: "Phase L3 Current"
device_class: current
state_class: measurement
unit_of_measurement: "A"
state: "{{ (state_attr('sensor.ampohub_iot_gateway','i3')|float(0) / 1000) | round(3) }}"
# ---------- Frequency ----------
- name: "Mains Frequency"
device_class: frequency
state_class: measurement
unit_of_measurement: "Hz"
state: "{{ (state_attr('sensor.ampohub_iot_gateway','freq')|float(0) / 100) | round(2) }}"
# ---------- Active Power (per phase & total) ----------
- name: "L1 Active Power"
device_class: power
state_class: measurement
unit_of_measurement: "W"
state: "{{ ((state_attr('sensor.ampohub_iot_gateway','p1')|float(0) / 1000) | abs) | round(0) }}"
- name: "L2 Active Power"
device_class: power
state_class: measurement
unit_of_measurement: "W"
state: "{{ ((state_attr('sensor.ampohub_iot_gateway','p2')|float(0) / 1000) | abs) | round(0) }}"
- name: "L3 Active Power"
device_class: power
state_class: measurement
unit_of_measurement: "W"
state: "{{ ((state_attr('sensor.ampohub_iot_gateway','p3')|float(0) / 1000) | abs) | round(0) }}"
- name: "Total Active Power"
device_class: power
state_class: measurement
unit_of_measurement: "W"
state: "{{ ((state_attr('sensor.ampohub_iot_gateway','pt')|float(0) / 1000) | abs) | round(0) }}"
# ---------- Neutral Current (A) ----------
- name: "Neutral Current"
device_class: current
state_class: measurement
unit_of_measurement: "A"
state: "{{ (state_attr('sensor.ampohub_iot_gateway','in')|float(0)) }}"
# Split signed power into import/export (Energy Dashboard likes separate flows)
- name: "Grid Power Import"
device_class: power
state_class: measurement
unit_of_measurement: "W"
# If your device uses negative for import, flip sign here:
state: >-
{% set p = (state_attr('sensor.ampohub_iot_gateway','pt')|float(0) / 1000) %}
{{ (0 - p) if p < 0 else 0 }}
- name: "Grid Power Export"
device_class: power
state_class: measurement
unit_of_measurement: "W"
state: >-
{% set p = (state_attr('sensor.ampohub_iot_gateway','pt')|float(0) / 1000) %}
{{ p if p > 0 else 0 }}
# ---------- Energy (cumulative) ----------
# If et is Wh, convert to kWh and mark as total_increasing for Energy Dashboard
- name: "Total Energy"
device_class: energy
state_class: total_increasing
unit_of_measurement: "kWh"
state: "{{ ((state_attr('sensor.ampohub_iot_gateway','et')|float(0) / 1000) | abs) | round(3) }}"To have historical graphs available in my dashboard, I created the following Utility_meter sensors as well:
utility_meter:
grid_daily:
source: sensor.total_energy
cycle: daily
delta_values: true
grid_monthly:
source: sensor.total_energy
cycle: monthly
delta_values: trueRestart your Home Assistant to take effect.
Creating dashboard in Home Assistant to show AmpoHub data
Create a new dashboard and go to the RAW editor. Paste the following into the editor:
views:
- title: AmpoHub
sections:
- type: grid
cards:
- type: heading
heading: Raw Data
heading_style: title
- type: entities
entities:
- sensor.ampohub_iot_gateway
title: Status
state_color: false
- graph: line
type: sensor
entity: sensor.mains_frequency
detail: 2
grid_options:
columns: full
- type: entities
entities:
- entity: sensor.phase_l1_voltage
- entity: sensor.phase_l1_current
- entity: sensor.l1_active_power
- type: entities
entities:
- entity: sensor.phase_l2_voltage
- entity: sensor.phase_l2_current
- entity: sensor.l2_active_power
- type: entities
entities:
- entity: sensor.phase_l3_voltage
- entity: sensor.phase_l3_current
- entity: sensor.l3_active_power
- type: tile
entity: sensor.neutral_current
vertical: false
features_position: bottom
grid_options:
columns: full
- type: entities
entities:
- entity: sensor.total_active_power
- entity: sensor.total_energy
- type: grid
cards:
- type: heading
heading: Graphs
heading_style: title
- type: history-graph
entities:
- entity: sensor.grid_daily
title: Daily Power Usage
hours_to_show: 24
logarithmic_scale: false
grid_options:
columns: full
- type: history-graph
entities:
- entity: sensor.grid_monthly
title: Monthly Power Usage
grid_options:
columns: full
hours_to_show: 720
column_span: 2
- type: grid
cards:
- type: heading
heading: Current Usage Summary
heading_style: title
- type: gauge
entity: sensor.total_active_power
needle: false
- type: gauge
entity: sensor.total_energy
type: sections
max_columns: 4
cards: []
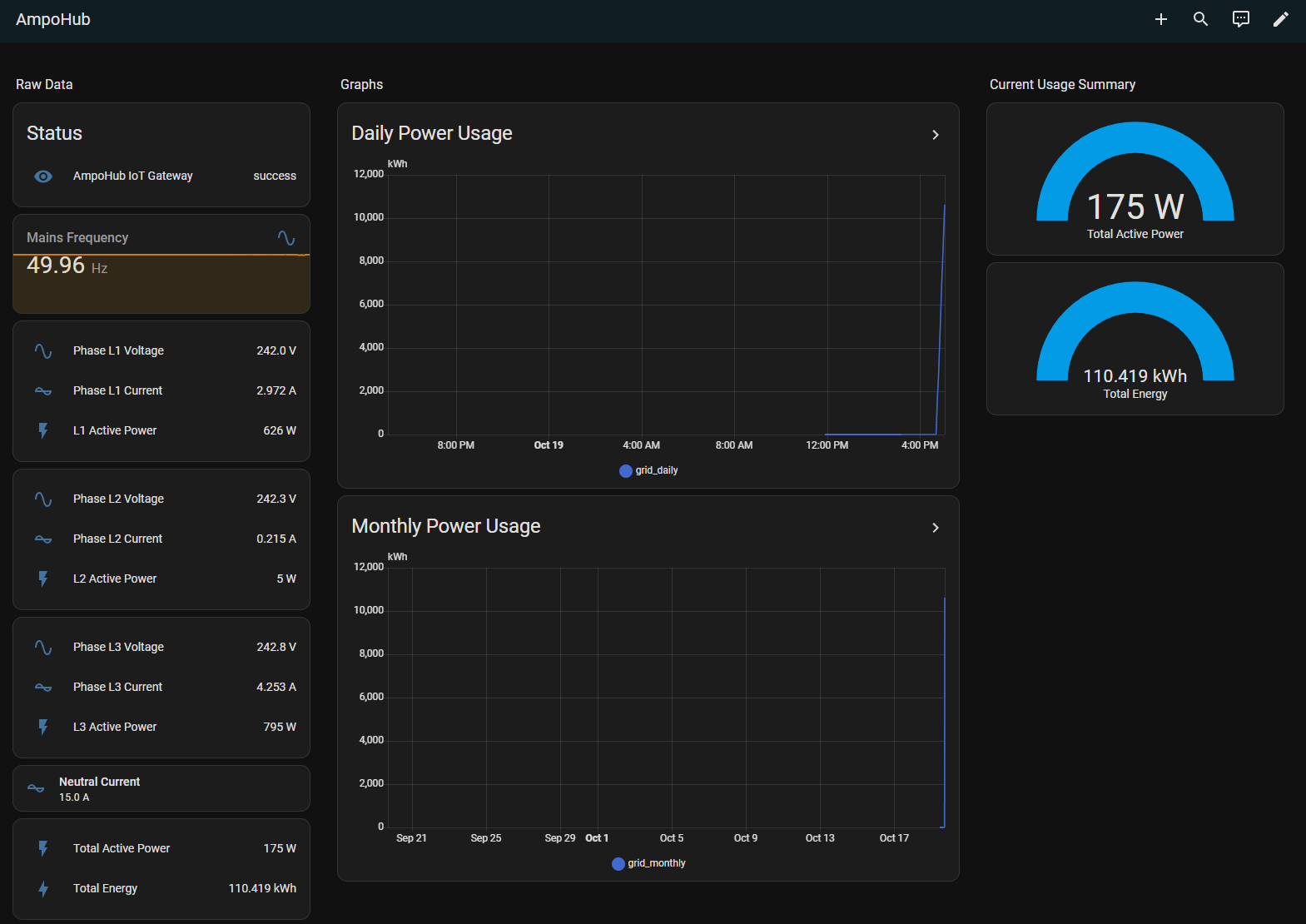
Once that is done, you should be able to see a dashboard similar to this:
Github Repository
To view the files mentioned in my post, visit my GitHub Repository at https://github.com/alexlogy/homeassistant-ampohub.